Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to insulin deficiency or resistance. Here are its key clinical features:
1. Classic Symptoms
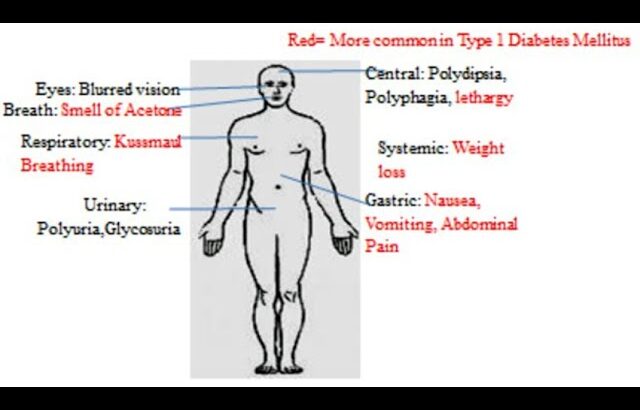
Polyuria (excessive urination)
Polydipsia (excessive thirst)
Polyphagia (excessive hunger)
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and weakness
2. Acute Complications
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – More common in Type 1 Diabetes, characterized by fruity breath, rapid breathing, nausea, and confusion.
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) – Seen in Type 2 Diabetes, leading to severe dehydration and altered mental status.
3. Chronic Complications
Microvascular Complications:
Diabetic Retinopathy – Vision loss due to retinal damage.
Diabetic Nephropathy – Kidney damage leading to proteinuria.
Diabetic Neuropathy – Nerve damage causing numbness, tingling, and pain.
Macrovascular Complications:
Cardiovascular Disease – Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) – Poor circulation leading to slow wound healing.
4. Other Clinical Signs
Skin Changes – Acanthosis nigricans (darkened skin patches), diabetic dermopathy.
Frequent Infections – Increased susceptibility to urinary tract infections, fungal infections, and slow-healing wounds.
#DiabetesMellitus